-$$ to enforce
-keeps police from doing other, more productive things
-->large bureaucracies are resistant to change; U.S. prison system the largest in the world
-->U.S. spends $33 bill, arrest 1.5 mill people annually to enforce the drug prohibition
-Lots of effort, yet drug use continues
If drug prices had risen? Real price to end user has actually fallen in past decades
-Drug interactions have strong correlation w/ violent crime rate and drug law enforcement
-elim drug prohibition, would reduce the drug homicide rate
ex: 40,000 deaths in Mexican drug war
-people kill each other to get demand
-cross border violence
ex: California's 3 strike law: 3 chances to be caught with marijuana then get 15-20 years in prison
-Completely reduces marginal cost of beating up/killing someone who know to 0
-cost isn't higher b/c end up in prison if knowledge of substance and you get out
-->lowered marginal cost of committing the next worst crime, already going to jail
Why drug law came into being when they did?
-recession, depression, prohibition happens when economy bad?
ex: Before 1930, no outright call for the replacement of the 18th Amendment.
How did it gain momentum?
Great Depression, ruined the federal tax income
Prior to 1913, 1/3 of gov't revenue came from liquor tax
-1920, income tax brought in more $ so Congress could allow temperance movement
--> $$ important!!!
-1930, income tax plummeted, awful recession
-Used liquor sales in 1934 to raise revenues
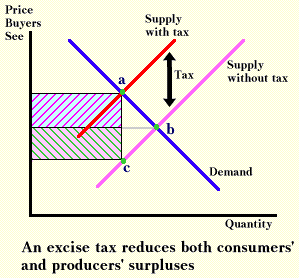
Economic Incidence of Supply & Demand
Application: Taxation
Consider: Odd, tax not benefit or cost, it is merely a transaction; doesn't help or hurt
-taxes just transfer
-$ to gov't a benefit? only good if dollars spend well
Excise Tax: legal liability for a tax is on the seller
-the seller has to write the check to the gov't
-customers not liable
Example: tax on millions of packs of bubblegum
Initial Equilib: P* = $3
After Tax:
P buyers =$3.75
P sellers = $2.75
Qt = 2.75 mill, Taxes $2.75 mill
| | Buyers | Sellers |
| Initial P | $3.00 | $3.00 |
| Final P | $3.75 | $3.75 |
| Tax Paid | --- | $1.00 ->$2.75 |
| Economic Burden | 75 cents | ? |
-Tax is one suppliers, tax affects the supply curve, $1 per pack
-->shift supply curve UP by amount of the tax
-new equilib of 9
Notice, tax increased by $1, BUT
1st Result: price doesn't incr. by the amount of the tax
-price went up 75 cents
2nd Result: How much $ raised by the gov't?
Wanted $3 mill, but generated $2.75 mill
Why Does This Happen?
Drives a wedge btwn buyers & sellers
-prevented other good transactions
-tax gets in the way; use $1 to gain 70 cents
--> tax greater than the value of the transaction, transfer won't happen
Problems with taxes:
-less wealth, fewer jobs, less businesses
-value of forgone transaction that would have happened absent of the tax
-bad if tax inefficiently
Cost resources to collect taxes
-Pay for peopel who administer, monitor & process the tax
-spend 41 cent per $100 tax collected to have the IRS, 115,000 people producing nothing of value
-dead weight separate from fraud
Fraud: cheat on taxes, spend resources trying to cheat than doing something beneficial

No comments:
Post a Comment